
DISCLAIMER
Please note: The information contained in this section is restricted to medical and healthcare practitioners for general education and information purpose only

Following signs should be assessed and require thorough assessment:
Reference: Bush LM. Fever in adults. MSD Manual. Sep 2022. Accessed on Nov 2, 2022, from https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/home/infections/biology-of-infectious-disease/fever-in-adults
The primary goal: Relieve the discomfort commonly associated with fevers by reducing temperature to normal body temperature.
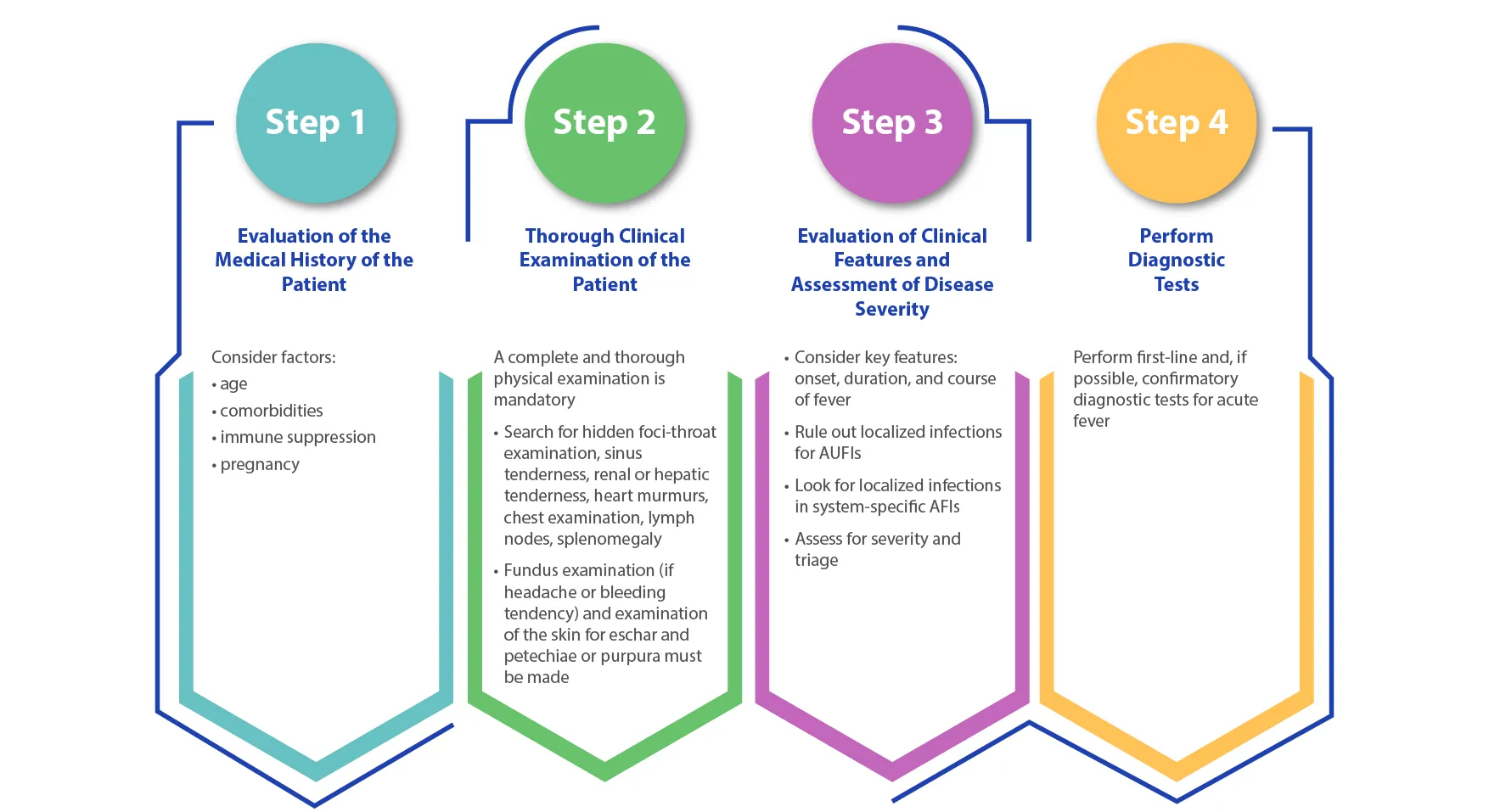
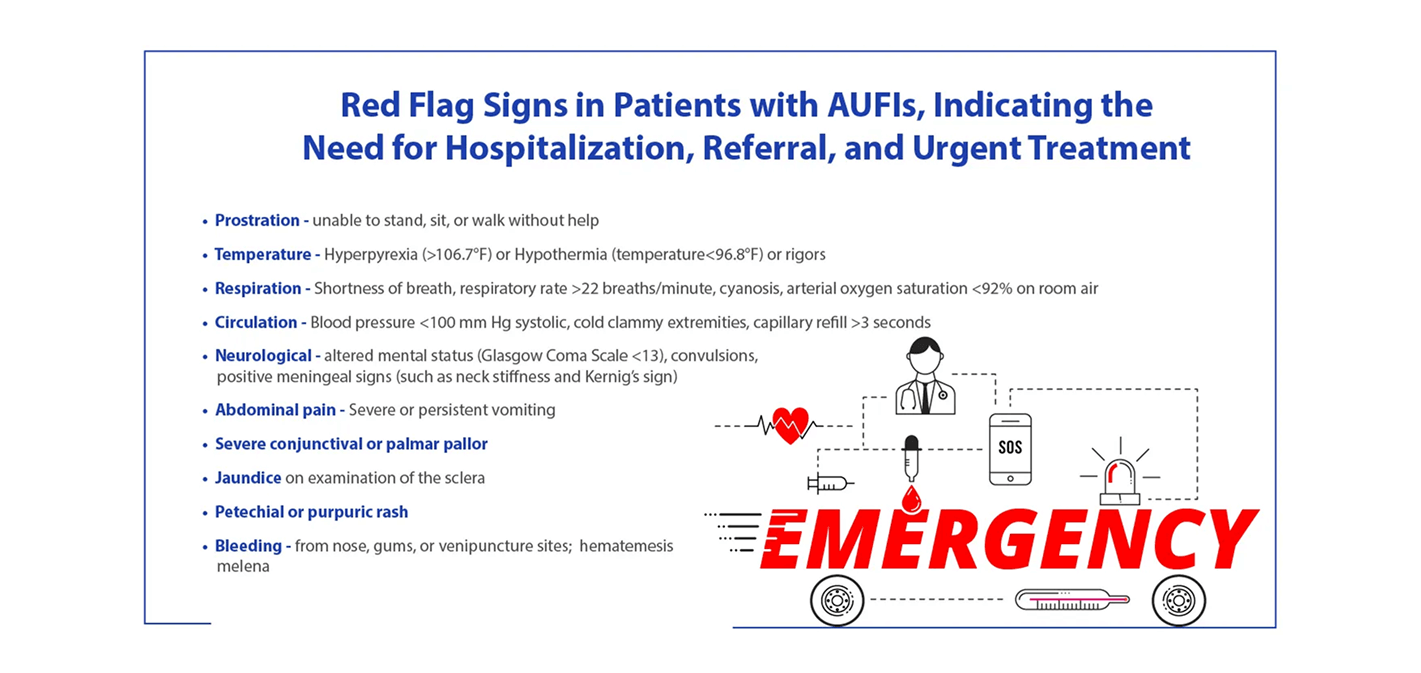
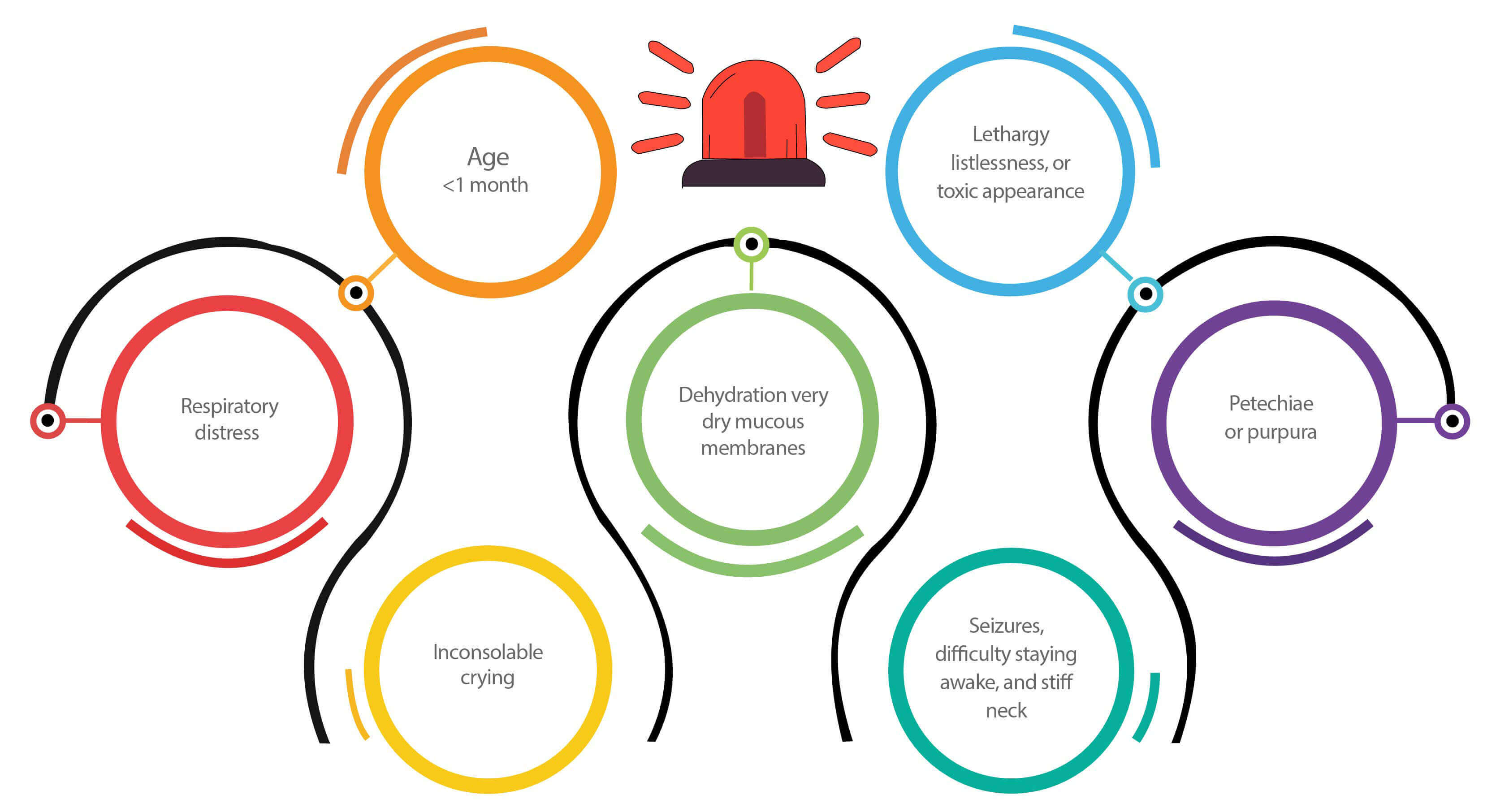
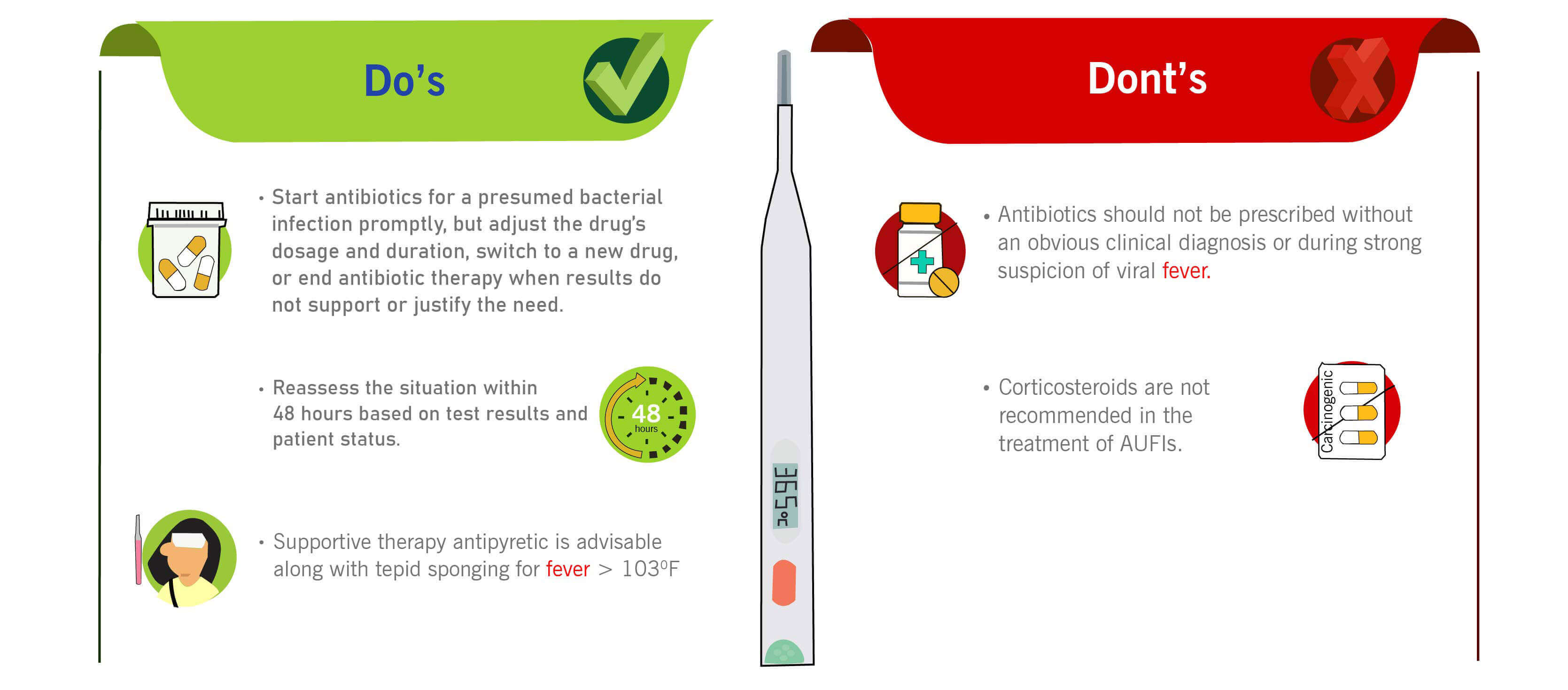
Reference: Stepwise guide for diagnosis and management of acute fever in primary care. Accessed on November 2, 2022, from https://www.ima-india.org/ima/pdfdata/Treatment-Algorithm-Flip-Chart-03122021.pdf


